gRPC: Revolutionizing Modern API Development
In the rapidly evolving landscape of distributed systems and microservices architecture, traditional REST APIs are increasingly showing their limitations. Enter gRPC, a high-performance, open-source universal RPC framework that's transforming how developers build and connect services across different platforms and languages.
What Makes gRPC Different
gRPC, originally developed by Google, represents a significant advancement over traditional API communication protocols. Unlike REST, which relies on HTTP/1.1 and JSON, gRPC utilizes HTTP/2 as its transport protocol and Protocol Buffers (protobuf) for serialization. This combination delivers substantial performance improvements and enables features that were previously complex to implement.
The framework's design philosophy centers around efficiency, type safety, and cross-language compatibility. By defining service contracts using Protocol Buffers, developers can generate client and server code in multiple programming languages from a single source of truth. This approach eliminates the ambiguity often found in REST API documentation and ensures consistent behavior across different implementations.
Core Architecture and Components
gRPC's architecture consists of several key components that work together to provide a robust communication framework. The Protocol Buffer compiler (protoc) generates code from service definitions, creating strongly-typed interfaces that eliminate runtime errors common in loosely-typed systems.
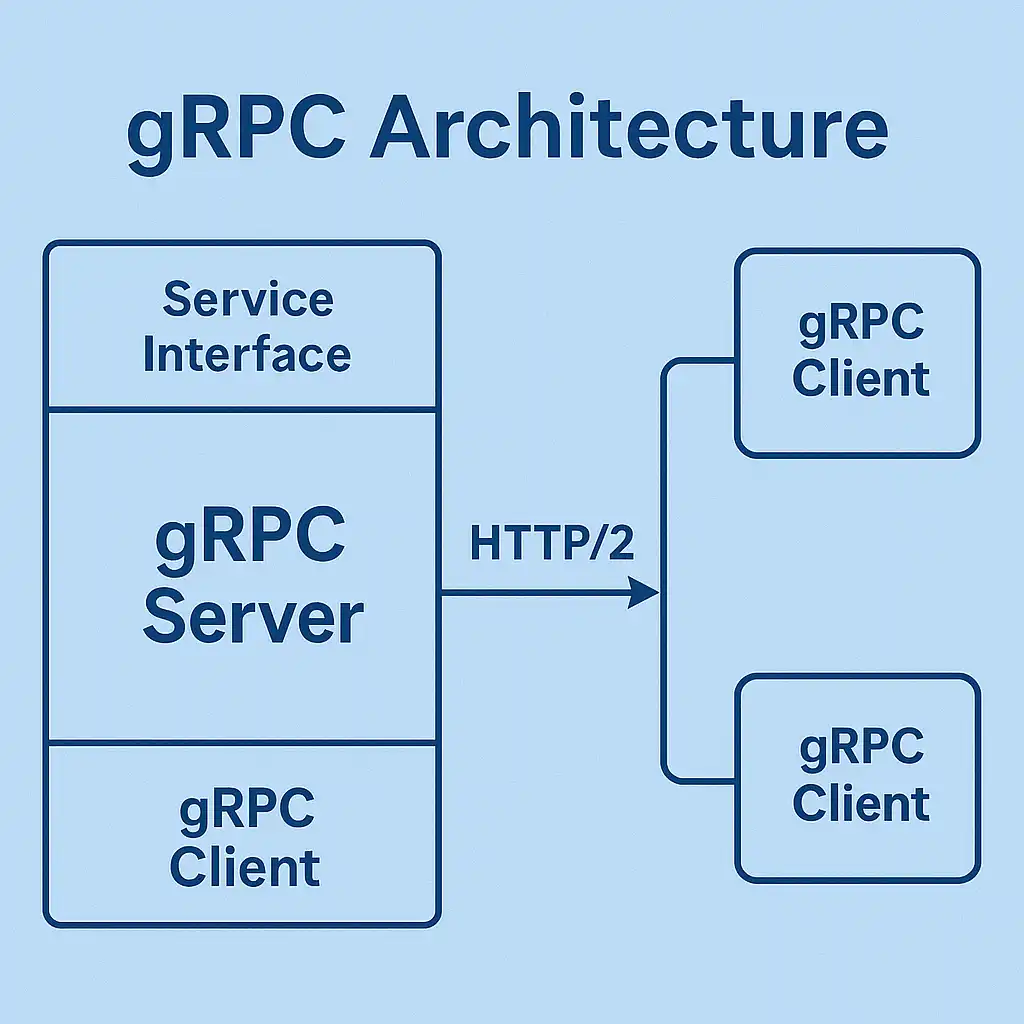
The service definition acts as a contract between client and server, specifying available methods, request/response types, and error handling mechanisms. This contract-first approach ensures that both parties understand the expected behavior before implementation begins, reducing integration issues and improving development velocity.
The underlying HTTP/2 transport provides features like multiplexing, server push, and header compression. These capabilities enable gRPC to handle multiple concurrent requests over a single connection, significantly reducing latency and improving resource utilization compared to traditional HTTP/1.1-based APIs.
Performance Advantages
The performance benefits of gRPC become apparent in high-throughput scenarios. Protocol Buffers' binary serialization format is significantly more compact than JSON, resulting in smaller message sizes and reduced bandwidth consumption. This efficiency is particularly valuable in mobile applications and IoT scenarios where network resources are constrained.
HTTP/2's multiplexing capabilities eliminate the head-of-line blocking issues that plague HTTP/1.1 connections. Multiple requests can be processed simultaneously over a single connection, reducing the overhead associated with establishing multiple TCP connections. This improvement is especially noticeable in microservices architectures where services frequently communicate with each other.
The strongly-typed nature of Protocol Buffers enables compile-time validation, catching errors early in the development process. This type safety extends to the wire format, ensuring that data corruption during transmission is detected and handled appropriately.
Communication Patterns
gRPC supports four distinct communication patterns, each suited to different use cases and requirements. Understanding these patterns is crucial for designing effective distributed systems.
Unary RPCs
represent the simplest form of gRPC communication, similar to traditional function calls. The client sends a single request and receives a single response. This pattern works well for simple query operations and CRUD operations where immediate responses are required.
Server Streaming RPCs
enable servers to send multiple responses to a single client request. This pattern is ideal for scenarios like real-time data feeds, file downloads, or any situation where the server needs to push data to the client over time.
Client Streaming RPCs
allow clients to send multiple requests before receiving a single response from the server. This pattern is useful for scenarios like file uploads, batch processing, or collecting sensor data over time.
Bidirectional Streaming RPCs
enable both client and server to send multiple messages in both directions simultaneously. This pattern supports complex interactions like real-time chat applications, collaborative editing, or any scenario requiring continuous bidirectional communication.
Implementation Considerations
Successful gRPC implementation requires careful attention to several key areas. Service design should follow established patterns and conventions to ensure maintainability and interoperability. Breaking changes to service definitions can impact existing clients, so versioning strategies must be established early in the development process.
Error handling in gRPC differs from traditional HTTP error codes. The framework provides a rich set of status codes and the ability to include detailed error information in responses. Proper error handling ensures that clients can respond appropriately to various failure scenarios.
Security considerations are paramount in distributed systems. gRPC provides built-in support for TLS encryption and authentication mechanisms. Integration with existing authentication systems like OAuth2 or JWT tokens requires careful planning to ensure security without compromising performance.
Why is gRPC So Fast?
1. HTTP/2
Look, this is huge. While REST APIs are typically stuck with the HTTP/1.1`s request and response limitations, but gRPC leverages HTTP/2 multiplexing. Multiple request can be on a same boat simultaneously over a single connection. No more connection pooling headaches or head of line blocking.
2. Binary serialisation
JSON is my best friend and I know yours too which is great for us but not for machines. In this what happens, protocol buffers create much smaller payloads and I have seen 60 to 80 % size reduction compared to equivalent JSON. Smaller payloads means faster network transmission and less bandwidth usage, right!
3. Compression
As we know, gRPC compress data automatically. By combining with the compact binary format, you are looking at the best efficient data transfer. This is especially notable In mobile applications or when we are dealing with limited bandwidth.
4. Streaming
Instead of multiple round trips, we can stream data continuously. Consider scenarios like real time analytics or live updates, this eliminates the latency of establishing new connections repeatedly.
Integration Testing With Keploy
Keploy provide the support for gRPC integration testing and it is definitely a great for testing gRPC services.
It watches your gRPC calls while your app is running and automatically creates test cases from real interactions. I'm not kidding, you just use your application normally, and it records everything. Then later, it can replay those exact same interactions as tests. You can read about integration testing with keploy here.
The dependency thing is genius: Remember how we always struggle with mocking databases and external services in our tests? Keploy captures all of that too. So when it replays your tests, it uses the exact same data that was returned during the recording. So basically, it doesn't spend more hours setting up test databases or writing complex mocks.
Catching regressions: You know, this is where it outperformed others. When you make changes to your gRPC services, Keploy compares the new responses with what it recorded before. If something changes unexpectedly, it flags it immediately.
Keploy represents the future of API testing that is intelligent, automated, and incredibly developer friendly. So, If you're building gRPC services, definitely check out what Keploy can do for your testing workflow. It's one of those tools that makes you wonder how you ever tested APIs without it.
Benefits of gRPC
The benefits are quite interesting:
-
Performance improvements are real and measurable.
-
Development velocity increases because of the strong typing and code generation.
-
Cross language interoperability becomes trivial.
-
Operational complexity decreases because of standardized health checks, metrics and tracing
The ecosystem of gRPC is rich, too. There are interceptors for logging, authentication, and monitoring. In this, cloud providers also offer native support.
Best Practices for Production
Deploying gRPC services in production requires attention to monitoring, logging, and operational considerations. Traditional HTTP-based monitoring tools may not provide adequate visibility into gRPC service behavior, necessitating specialized tooling.
Connection management becomes crucial in high-load scenarios. Proper connection pooling and lifecycle management ensure optimal resource utilization and prevent connection exhaustion issues.
Graceful degradation strategies help maintain service availability during partial failures. Circuit breaker patterns and timeout configurations prevent cascading failures that could impact the entire system.
Future Developments
The gRPC ecosystem continues to evolve with new features and improvements. gRPC-Web enables browser-based clients to communicate with gRPC services, expanding the framework's applicability to web applications.
Performance optimizations continue to improve efficiency, with new compression algorithms and protocol enhancements reducing overhead and improving throughput. These improvements benefit all gRPC users without requiring code changes.
The growing ecosystem of tools and libraries makes gRPC increasingly accessible to developers. IDE integrations, debugging tools, and testing frameworks reduce the learning curve and improve developer productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the main difference between gRPC and REST?
gRPC uses HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers for faster, more efficient communication, while REST typically uses HTTP/1.1 and JSON. gRPC offers better performance, built-in code generation, and stronger type safety, but REST has broader ecosystem support and is more familiar to most developers.
Can I use gRPC with existing HTTP/JSON APIs?
Yes, gRPC services can coexist with REST APIs. Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach, using gRPC for internal service communication while maintaining REST APIs for external clients or legacy systems.
How does gRPC handle versioning?
gRPC uses Protocol Buffers' backward compatibility features. You can add new fields and methods without breaking existing clients, but removing or changing existing fields requires careful migration planning.
Is gRPC suitable for mobile applications?
Absolutely. gRPC's efficient binary protocol and HTTP/2 multiplexing make it ideal for mobile environments where bandwidth and battery life are concerns. The smaller message sizes and reduced connection overhead provide significant benefits.
What programming languages support gRPC?
gRPC supports most major programming languages including Go, Java, Python, C++, C#, Node.js, Ruby, PHP, and many others. The Protocol Buffer compiler generates idiomatic code for each supported language.