Software Testing Life Cycle
Software Testing Life Cycle, more commonly known as STLC, is a process to test software applications to ensure they meet quality standards, fulfill requirements, and perform as expected. STLC consists of several phases that guide the testing process from inception to completion, ensuring thorough testing and defect identification.
What are the Phases of Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
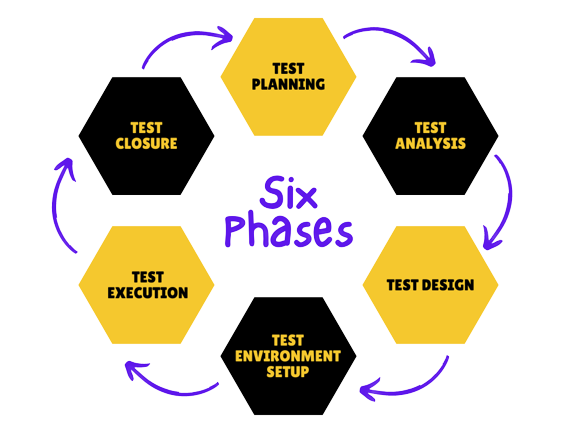
Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) comprises several phases that guide the testing process from inception to completion. The key phases include:
-
Requirement Analysis:
- Objective: Understand software requirements and define test objectives.
- Activities: Review requirements, identify testable features, and plan test strategy.
-
Test Planning:
- Objective: Define test scope, resources, and timelines.
- Activities: Develop test plan, determine testing types, and establish metrics.
-
Test Design:
- Objective: Create detailed test cases and scenarios.
- Activities: Write test cases, define test data, and prioritize tests.
-
Test Environment Setup:
- Objective: Prepare the testing infrastructure.
- Activities: Configure hardware, software, and test tools.
-
Test Execution:
- Objective: Execute test cases and identify defects.
- Activities: Run tests, log results, and capture evidence.
-
Defect Reporting:
- Objective: Document and prioritize defects.
- Activities: Report issues, classify severity, and assign to developers.
-
Defect Retesting and Regression Testing:
- Objective: Verify defect fixes and ensure no new issues arise.
- Activities: Re-execute failed tests, perform regression testing, and validate fixes.
-
Test Closure:
- Objective: Assess testing completion and readiness for release.
- Activities: Evaluate test results, generate reports, and obtain stakeholder sign-off.
What are some common Practices in STLC ?
- Automation Testing: Automate repetitive tests to save time and improve accuracy.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Integrate testing into development cycles for early defect detection.
- Risk-Based Testing: Prioritize tests based on potential impact and likelihood of failure.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate software performance under various conditions and loads.
How Keploy helps in accelrating the Software Testing Life Cycle process?
Keploy enhances the STLC with its advanced features tailored for modern software testing needs:
-
Automated Test Case Generation: Keploy automates the creation of test cases, reducing manual effort and ensuring comprehensive coverage.
-
Error Debugging and Analysis: Built-in tools pinpoint errors quickly, accelerating troubleshooting and resolution.
-
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines: Seamlessly integrates with CI/CD workflows, automating test execution and ensuring consistent testing practices.
-
Collaboration and Documentation: Provides a centralized platform for team collaboration, test case documentation, and knowledge sharing.
Conclusion
Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) is integral to ensuring software quality and reliability throughout development. By following structured phases—from requirement analysis to test closure—organizations can mitigate risks, improve software performance, and deliver value to stakeholders. Tools like Keploy further enhance STLC by automating testing processes, accelerating defect detection, and fostering collaboration among development teams.
Incorporating STLC best practices and leveraging advanced testing tools empower organizations to achieve higher quality standards, enhance customer satisfaction, and maintain competitive advantage in the dynamic software landscape.
FAQs
1. What are the key phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle?
- Answer: The key phases include Requirement Analysis, Test Planning, Test Design, Test Execution, Defect Reporting, Defect Retesting, Regression Testing, and Test Closure.
2. Why is STLC important in software development?
- Answer: STLC ensures software quality, identifies defects early, supports reliable software releases, and aligns testing efforts with business goals.
3. How does automation impact STLC?
- Answer: Automation streamlines testing processes, increases test coverage, reduces time-to-market, and enhances overall testing efficiency.
4. What is regression testing in STLC?
- Answer: Regression testing ensures that recent code changes have not adversely affected existing functionalities. It verifies system stability after modifications.
5. What role does test documentation play in STLC?
- Answer: Test documentation serves as a reference for test cases, results, and strategies. It aids in knowledge transfer, compliance, and future testing cycles.
6. How can STLC be customized for agile development?
- Answer: In agile environments, STLC phases are iterative and adaptable. Testing occurs continuously, aligning with short development cycles and frequent releases.