What is Keploy?
Keploy creates backend API tests with built-in-mocks or stubs by recording your application network calls making your testing process not only faster than unit tests but also incredibly efficient.
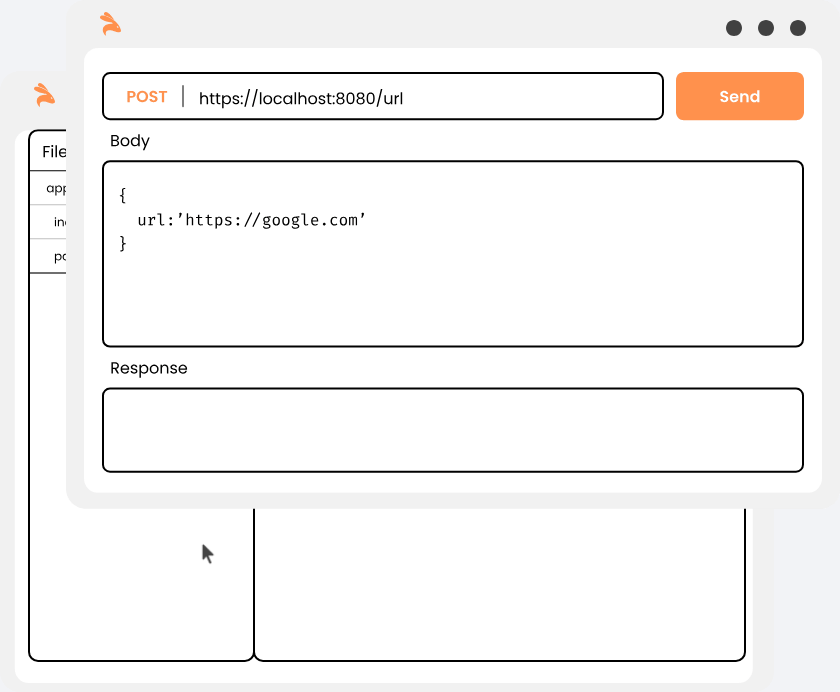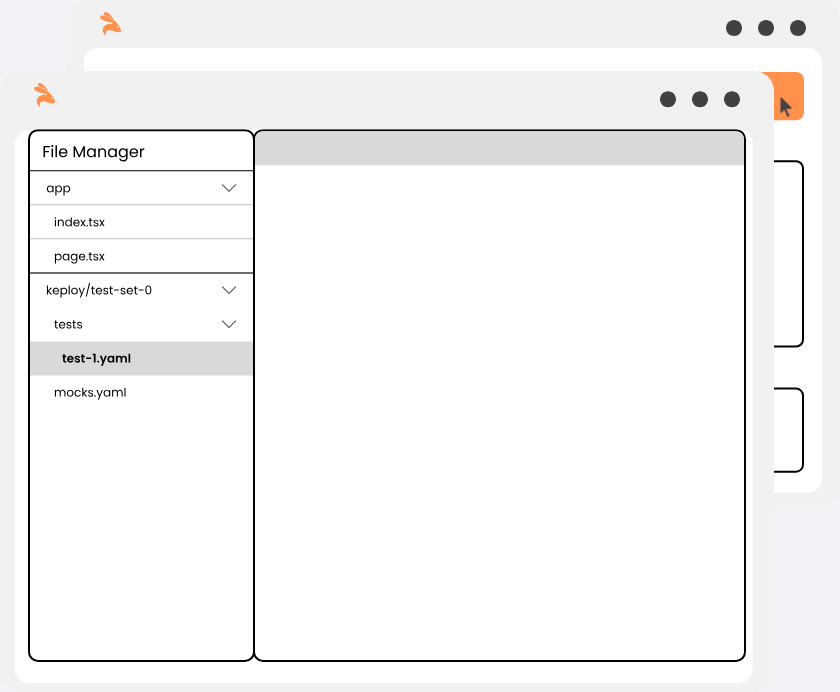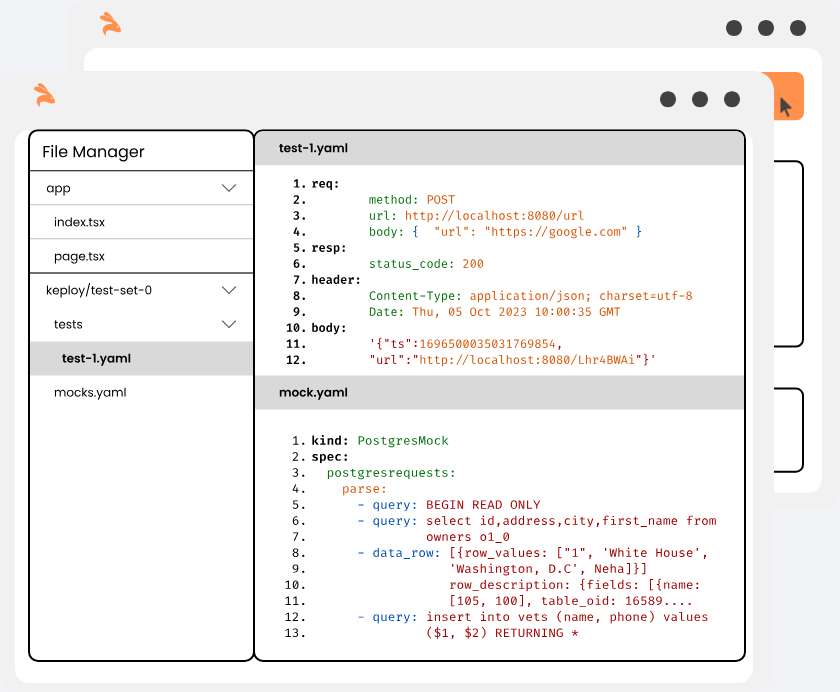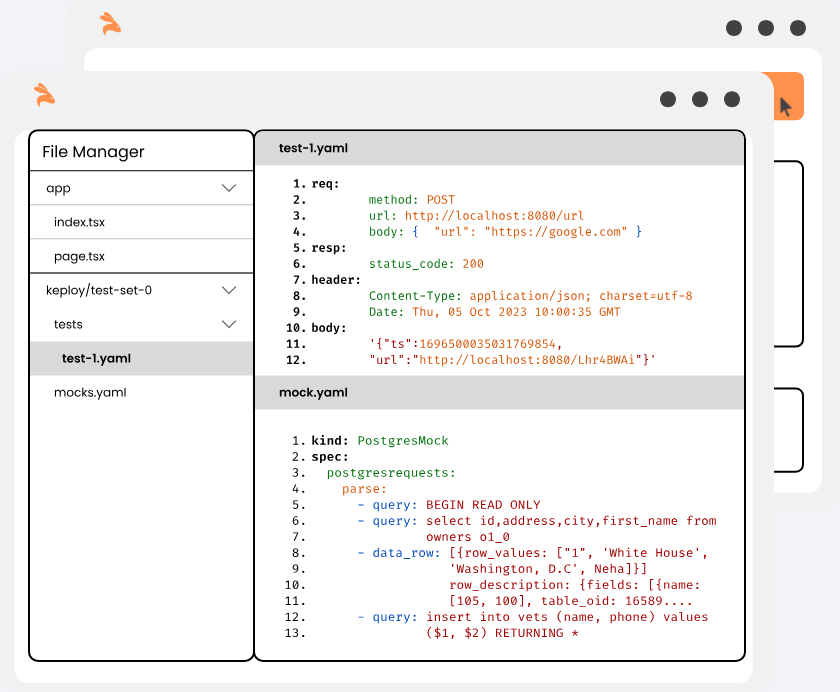
Keploy acts a proxy in your application that captures and replays all network interaction served to application from any source.
Step 1 : Record Unique Network Interactions as Test Case
Once you start the application in record mode to capture API calls as test cases.
Now, when the application serves an API, all the unique network interactions are stored within Keploy server as a test-case.
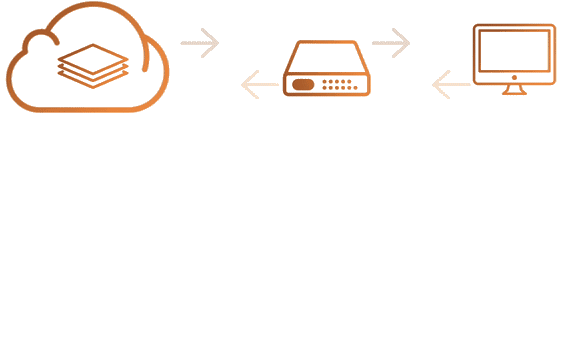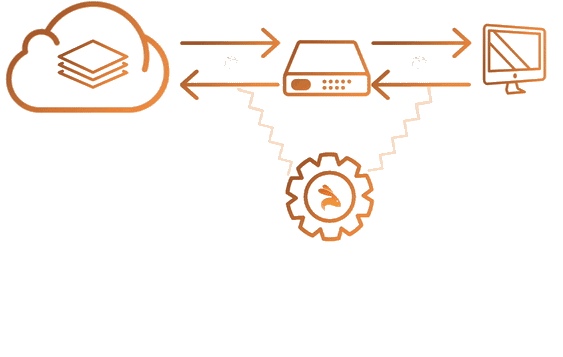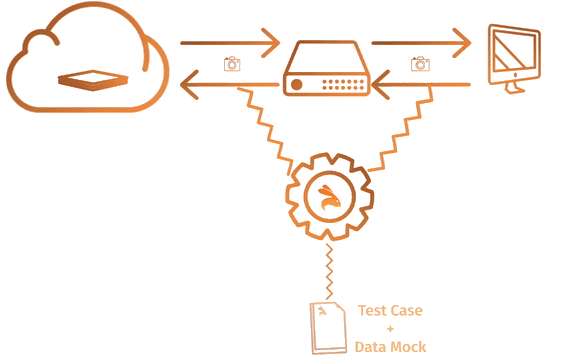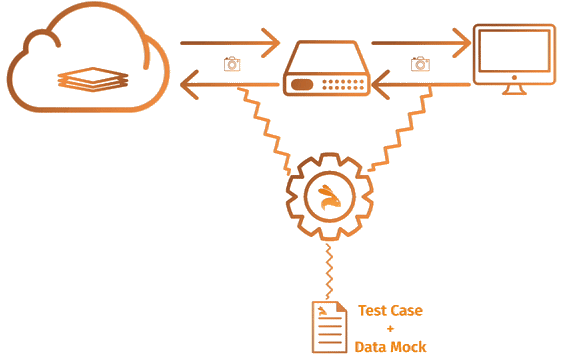
Step 2 : Replay Test-Cases
Let's say you developed new application version(v2). To test locally, start the Keploy in test mode to replay all recorded API calls/test-cases previously captured in record-mode.
Now, when the application starts:
- Keploy will download all the previously recorded test-cases/API calls with a 5 sec delay(configurable application build time).
- When the application will try to talk to any dependencies like DBs, Routers, vendor services, Keploy will intercept and provide the previously recorded dependency response.
Note: You didn't need to setup test-environment here. 🙅🏻♀️
- Keploy will compare the API response to the previously captured response and a report will be generated on the Keploy console.
You can test with Keploy locally or can integrate Keploy with popular testing-frameworks and existing CI pipelines.
Note: You can generate test cases from any environment which has all the infrastructure dependencies setup. Please consider using this to generate tests from low-traffic environments first. The deduplication feature necessary for high-traffic environments is currently experimental.
Hope this helps you out, if you still have any questions, reach out to us .
Contact Us
If you have any questions or need help, please feel free to reach out to us at hello@keploy.io or reach out us on

