API Test Generator
🤖 Why AI for API Testing?
| API Testing Challenge | ROI & Impact |
|---|---|
| Edge-case, bugs, coverage flows gets missed | Higher test coverage across CRUD and failure scenarios |
| APIs change frequently, leading to broken tests | Self-healing keeps tests even when APIs evolves |
| 30–50% of time spent writing tests | 50–80% reduction in test creation Covers more edge cases within limited resources, time |
💥 Why Keploy? Not Other AI Testing Tools
| Capability | Keploy | Most AI Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Validated test execution | ✅ Runs and verifies each test before saving | ❌ Often generates unverified or broken tests |
| Full API flow coverage (Create → Update → Delete) | ✅ Supports complete multi-step flows | ❌ Focuses on isolated requests |
| Edge case & negative test generation | ✅ Auto-detects and generates edge cases | ⚠️ Limited or requires manual prompting |
| Replay across environments | ✅ Runs tests in dev, staging, CI with environment switching | ⚠️ Often environment-specific or hard-coded |
| Self-healing on API changes | ✅ Updates tests if API schema changes | ❌ No maintenance support |
| Flaky test detection | ✅ Re-runs tests to detect instability | ❌ Not supported |
| Collaboration & governance features | ✅ RBAC, audit trails, tagging, Git sync | ❌ Basic or missing |
| Works from real traffic or browser flows | ✅ Converts real traffic or frontend API interactions into tests | ⚠️ Most rely only on static specs |
🚀 Keploy's API Test Generator

AI-powered testing engine that turns your API specs or traffic into stable, end-to-end test suites — no scripts, mocks, or manual setup required.
It supports:
- Generate tests from OpenAPI, Postman, or curl commands
- Run tests in any environment (dev, staging, CI)
- Edit, group, or delete test cases in the UI
- Share test reports or integrate them into CI pipelines
- Detect flaky tests and self-heal them using AI
- Record API flows via Keploy’s Chrome extension
Every test includes:
- Accurate assertions based on real responses
- Full lifecycle coverage (create → mutate → delete)
- Deduplication and flaky test detection
- Self-healing for minor API changes
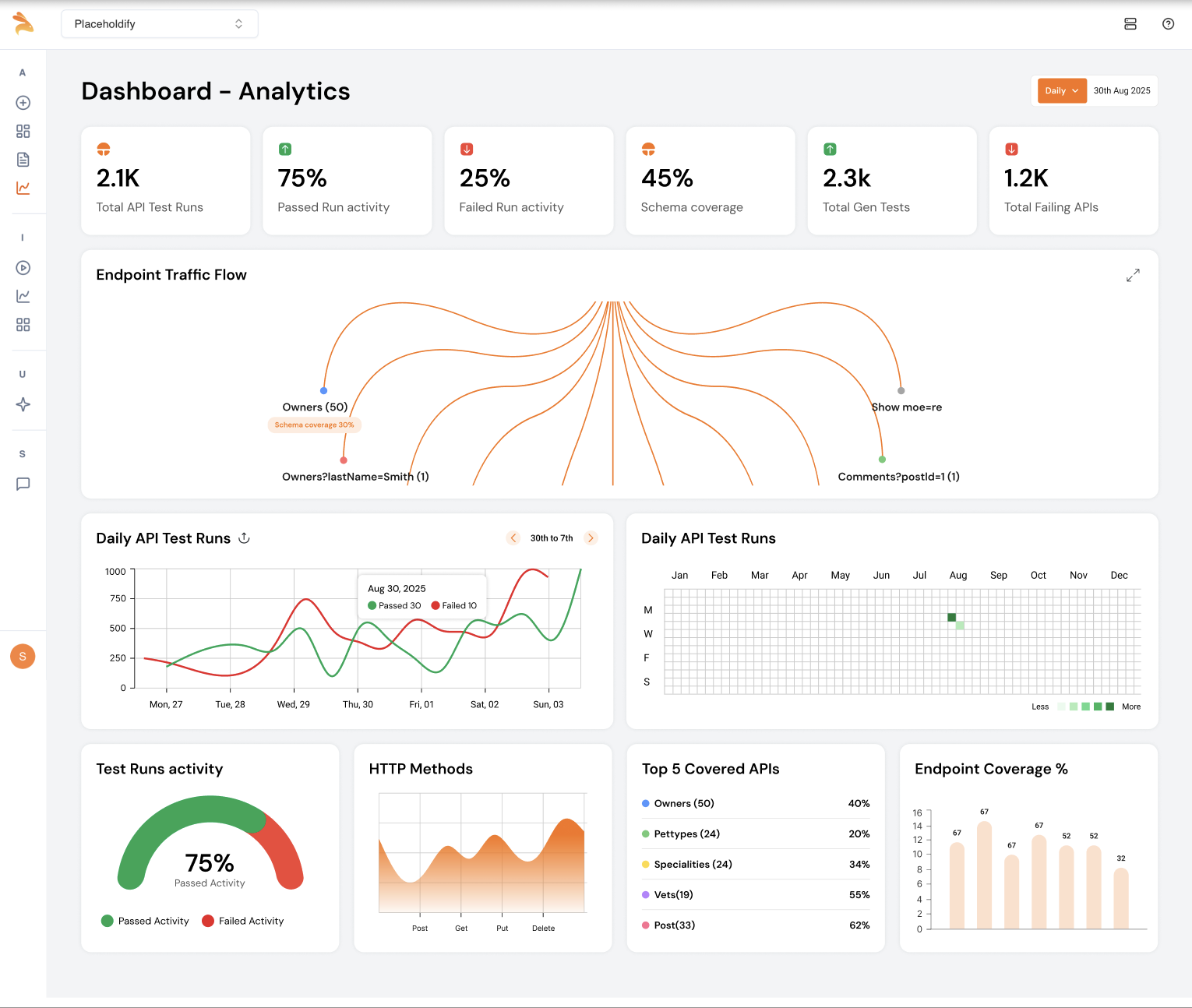
Whether you're a developer, SDET, or QA manager — Keploy helps you increase test coverage, reduce test debt, and ensure reliable releases across environments.
🛠️ How It Works
Keploy supports multiple ways to generate test cases depending on the API access method and input format. Choose the one that fits your workflow:
| Integration Method | When to Use | How Keploy Works? |
|---|---|---|
| Paste API Curls, Postman Collection, Schema/Swagger Try Now | You have OpenAPI/Swagger (YAML/JSON), Postman collection/curl, and a live public endpoint | Keploy hits multiple API cases to given endpoint and generate stable, validated tests with assertions. |
| Record via Keploy Chrome Extension | You don’t have specs but can interact with a web app for recording | Keploy captures real API calls made during UI actions and generates test cases with assertions. Adds edge cases and flow coverage automatically. |
| Use Keploy Local Agent Try Now | Your APIs are private or behind a firewall | Install the agent locally to securely test internal APIs without exposing them. No code changes required. |
✨ Key Features
- Self-healing tests: Keploy auto-updates tests on minor API changes
- Flaky test detection: Validates each test over multiple runs
- No redundant tests: Automatically deduplicates similar flows
- Environment reuse: Change the base URL to run the same test suite elsewhere
- One-click fix: Use AI to repair failing tests
✅ Best Practices
- Start with 5+ valid curl commands or a full spec
- Use the dashboard to clean, tag, or group test cases
- Validate flows in staging before pushing to CI
- Use assertions to cover both happy paths and edge cases
🚀 Try It Out
-
Go to keploy console API Test Generator
-
Add your API input or select a sample application (try demo)
-
Generate and review your test suite
-
You can run tests instantly, or export them into your pipeline.
🔒 Security & Compliance
Keploy is built with security-first principles and is compliant with major industry standards:

Your data and test traffic are handled securely, with the option to run Keploy entirely within your network using our self-hosted agent or BYOLLM infrastructure. To Learn more on our security page.