How to increase Code Coverage with Keploy
Code coverage is a metric that measures the extent to which the code in a program has been executed during testing. It is a valuable tool for software testers because it can help them to identify areas of the code that have not been tested and to ensure that the entire program has been adequately tested.
What is Code Coverage?
Code coverage is a metric used in software testing to measure the extent to which the source code of a program has been executed during automated testing. It quantifies the percentage of lines of code, branches, statements, or conditions that have been exercised by a test suite.
Code coverage refers to the extent to which your source code is tested by your test suite. It is a measure of how much of your code is executed when your tests are run. Code coverage is typically expressed as a percentage, with 100% code coverage meaning that every line of code in your program has been executed at least once during testing.
There are several types of code coverage metrics:
- Line Coverage: Measures the percentage of executable lines of code that have been executed by the test suite.
- Branch Coverage: Measures the percentage of decision points (branches) in the code that have been taken during testing. It ensures that both branches of every decision point (if-else statements, loops, etc.) have been executed.
- Statement Coverage: Similar to line coverage, but measures the percentage of individual statements that have been executed.
- Condition Coverage: Measures the percentage of Boolean expressions (conditions) that have been evaluated to both true and false during testing.
What is the need to perform Code Coverage?
Performing code coverage analysis is important because it provides insights into the effectiveness of testing efforts. Higher code coverage generally indicates a more comprehensive testing suite, which in turn can lead to greater confidence in the reliability and stability of the software.
It's analysis provides several benefits:
- Quality Assessment: Code coverage serves as a quantitative measure of the effectiveness of your testing efforts. It indicates how much of your codebase is being exercised by your test suite.
- Identifying Untested Code: Low code coverage highlights areas of the codebase that have not been adequately tested. Uncovered code may contain bugs or vulnerabilities that could go undetected in production.
- **Debugging Aid: Code coverage can help pinpoint areas of code that are not functioning as expected. If a test fails to cover a particular code segment, it may indicate a potential problem area that requires further investigation.
- Improving Test Suites: By identifying areas of low coverage, developers can focus their testing efforts on writing additional tests to increase coverage. This iterative process helps improve the overall quality and reliability of the software.
- Regulatory Compliance: In some industries, code coverage requirements may be mandated by regulatory standards or best practices. Achieving and maintaining adequate code coverage demonstrates a commitment to quality and compliance.
Get higher Code Coverage
Keploy has native integrations with your unit-testing libraries like go-test, jUnit, jest, pyTest. Keploy gives combined test-coverage and can also be integrated in existing CI pipelines easily within go-test, jUnit, jest, pyTest workflows.
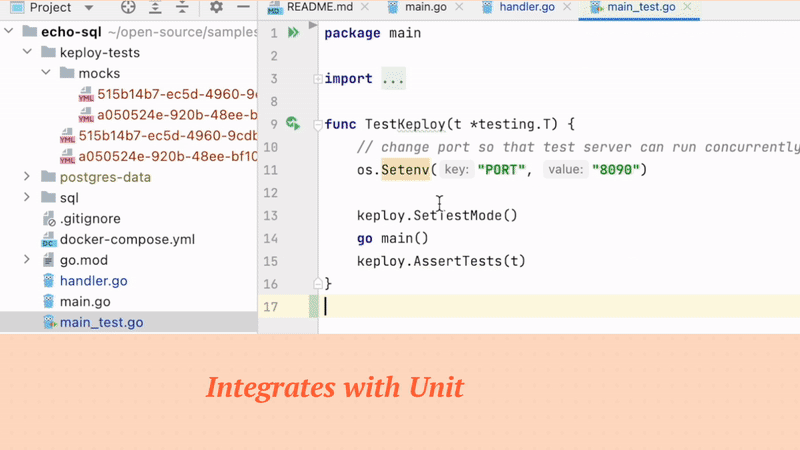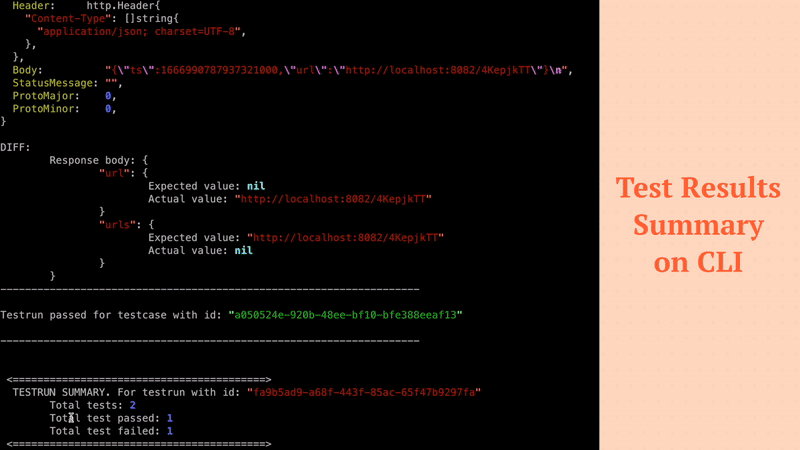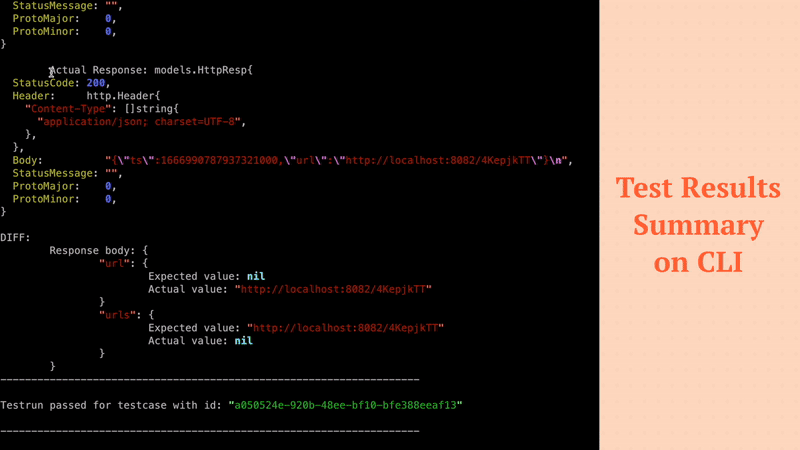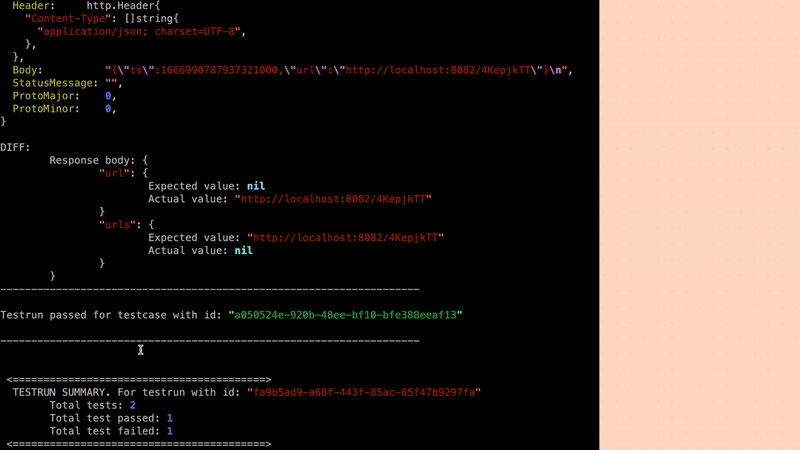
By generating additional tests that exercise different parts of your codebase, you can increase the percentage of code that is covered by your tests. For example, in case of NodeJS application you can use Jest. Jest provides a built-in code coverage tool that can help you measure the effectiveness of your tests and identify areas of the code that need additional testing. By adding Keploy SDK with Jest, you can easily generate test cases and increase your code coverage. Let's create a Keploy.test.js
const {expect} = require("@jest/globals");
const keploy = require("@keploy/sdk");
const timeOut = 300000;
describe(
"Keploy Server Tests",
() => {
test(
"TestKeploy",
(done) => {
const cmd = "npm start";
const options = {};
keploy.Test(cmd, options, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
done(err);
} else {
expect(res).toBeTruthy(); // Assert the test result
done();
}
});
},
timeOut
);
},
timeOut
);
Once last step is to add the jest configuration in package.json file.
scripts: {
"test": "jest --coverage --collectCoverageFrom='src/**/*.{js,jsx}'",
"coverage": "nyc npm test && npm run coverage:merge && npm run coverage:report",
"coverage:merge": "mkdir -p ./coverage && nyc merge ./coverage .nyc_output/out.json",
"coverage:report": "nyc report --reporter=lcov --reporter=text"
}
Now when let's the test cases with Jest, you can see the code coverage report generated by Jest.
npm test