Using Docker Compose 🐳
A Sample url shortener app to test Keploy integration capabilities using Echo and PostgreSQL
Don’t have Keploy installed yet?
Before running this sample, make sure Keploy is installed on your system.
👉 Go to Installation GuideClone a sample URL shortener app 🧪
git clone https://github.com/keploy/samples-go.git && cd samples-go/echo-sql
go mod download
First things first, update the postgres host on line 41 in main.go to postgres from localhost.
We will be using Docker compose to run the application as well as Postgres
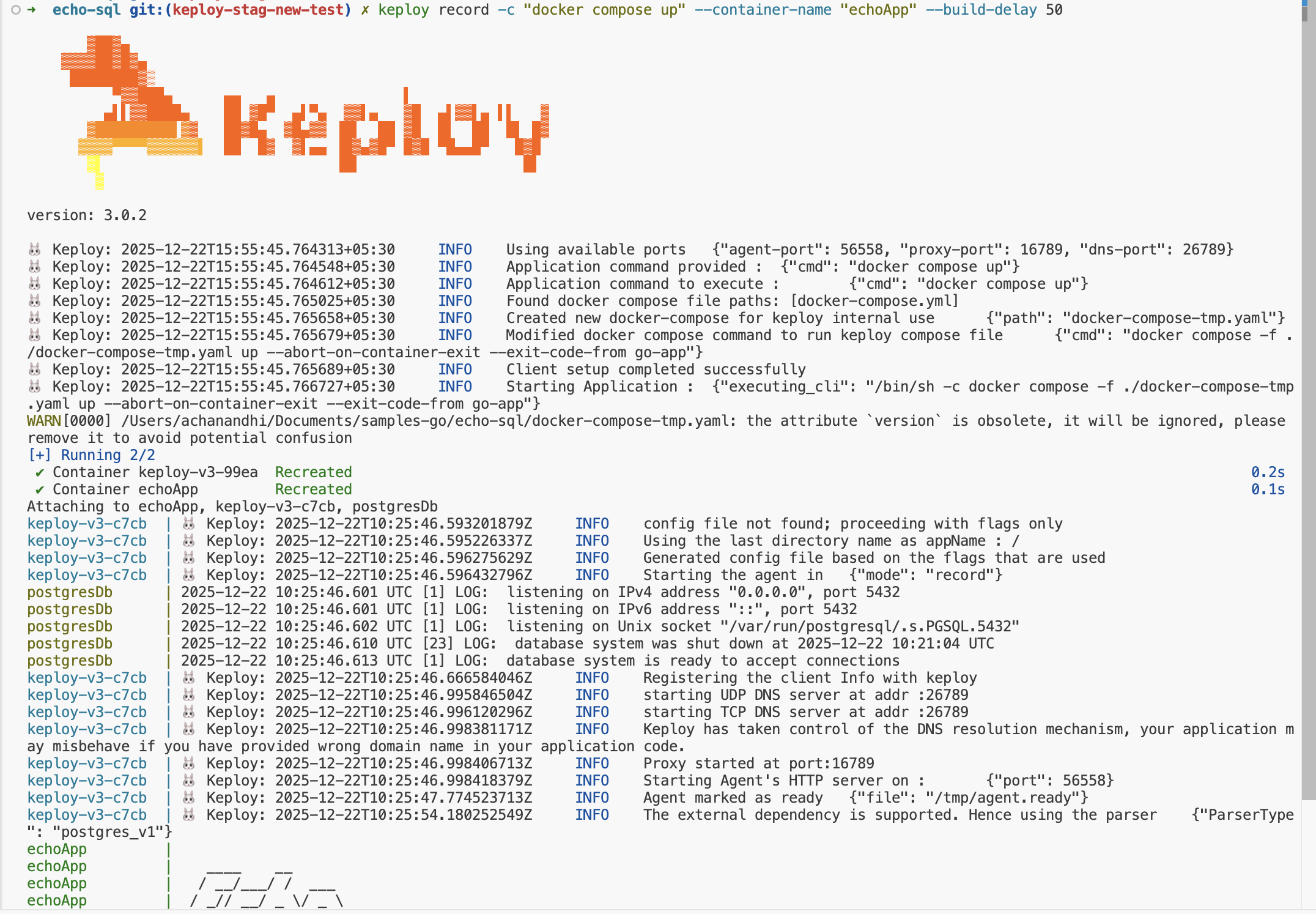
Lights, Camera, Record! 🎥
keploy record -c "docker compose up" --container-name "echoApp" --build-delay 50
--build-delayadds a buffer (in seconds) to allow images to build/pull and services to start before Keploy begins interception. If your services are already up, you can omit it.
Make API Calls using cURL command. Keploy with capture those calls to generate the test-suites containing testcases and data mocks.
Generate testcases
To generate testcases we just need to make some API calls. You can use Postman or simply curl
curl --request POST \
--url http://localhost:8082/url \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{
"url": "https://github.com"
}'
this will return the shortened url. The ts would automatically be ignored during testing because it'll always be different.
{
"ts": 1647802058801841100,
"url": "http://localhost:8082/GuwHCgoQ"
}
Redirect to original URL from shortened URL
1. By using Curl Command
curl http://localhost:8082/GuwHCgoQ
- Or by querying through the browser
http://localhost:8082/GuwHCgoQ
Now both these API calls were captured as editable testcases and written to keploy/tests folder. The keploy directory would also have mocks file that contains all the outputs of postgres operations. Here's what the folder structure look like:
Now, let's see the magic! ✨💫
Want to see if everything works as expected?
Run the Testcases
Time to put things to the test 🧪
keploy test -c "docker compose up" --container-name "echoApp" --build-delay 50 --delay 10
output should look like
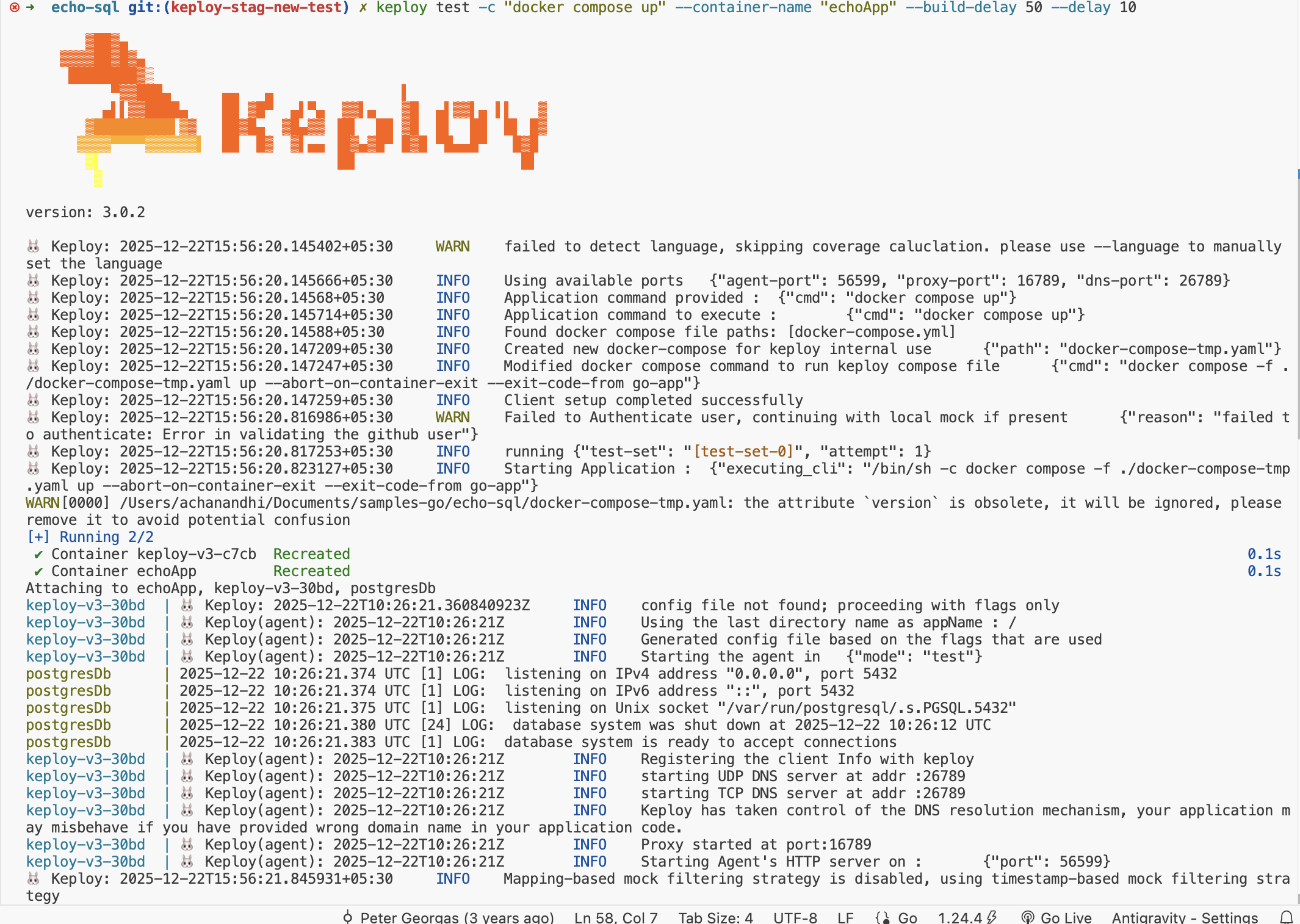
So no need to setup fake database/apis like Postgres or write mocks for them. Keploy automatically mocks them and, The application thinks it's talking to Postgres 😄
Wrapping it up 🎉
Congrats on the journey so far! You've seen Keploy's power, flexed your coding muscles, and had a bit of fun too! Now, go out there and keep exploring, innovating, and creating! Remember, with the right tools and a sprinkle of fun, anything's possible.😊🚀
Happy coding! ✨👩💻👨💻✨
Running App Locally on Linux/WSL 🐧
A Sample url shortener app to test Keploy integration capabilities using Echo and PostgreSQL
Don’t have Keploy installed yet?
Before running this sample, make sure Keploy is installed on your system.
👉 Go to Installation GuideClone a sample URL shortener app 🧪
git clone https://github.com/keploy/samples-go.git && cd samples-go/echo-sql
go mod download
We'll be running our sample application right on Linux, but just to make things a tad more thrilling, we'll have the database (Postgres) chill on Docker. Ready? Let's get the party started!🎉 Using the docker-compose file we will start our Postgres instance:-
docker-compose up postgres
Since we are using docker to run the application, we need to update the
postgreshost on line 41 inmain.go, update the host tolocalhost.
Now, we will create the binary of our application:-
go build -o echo-psql-url-shortener
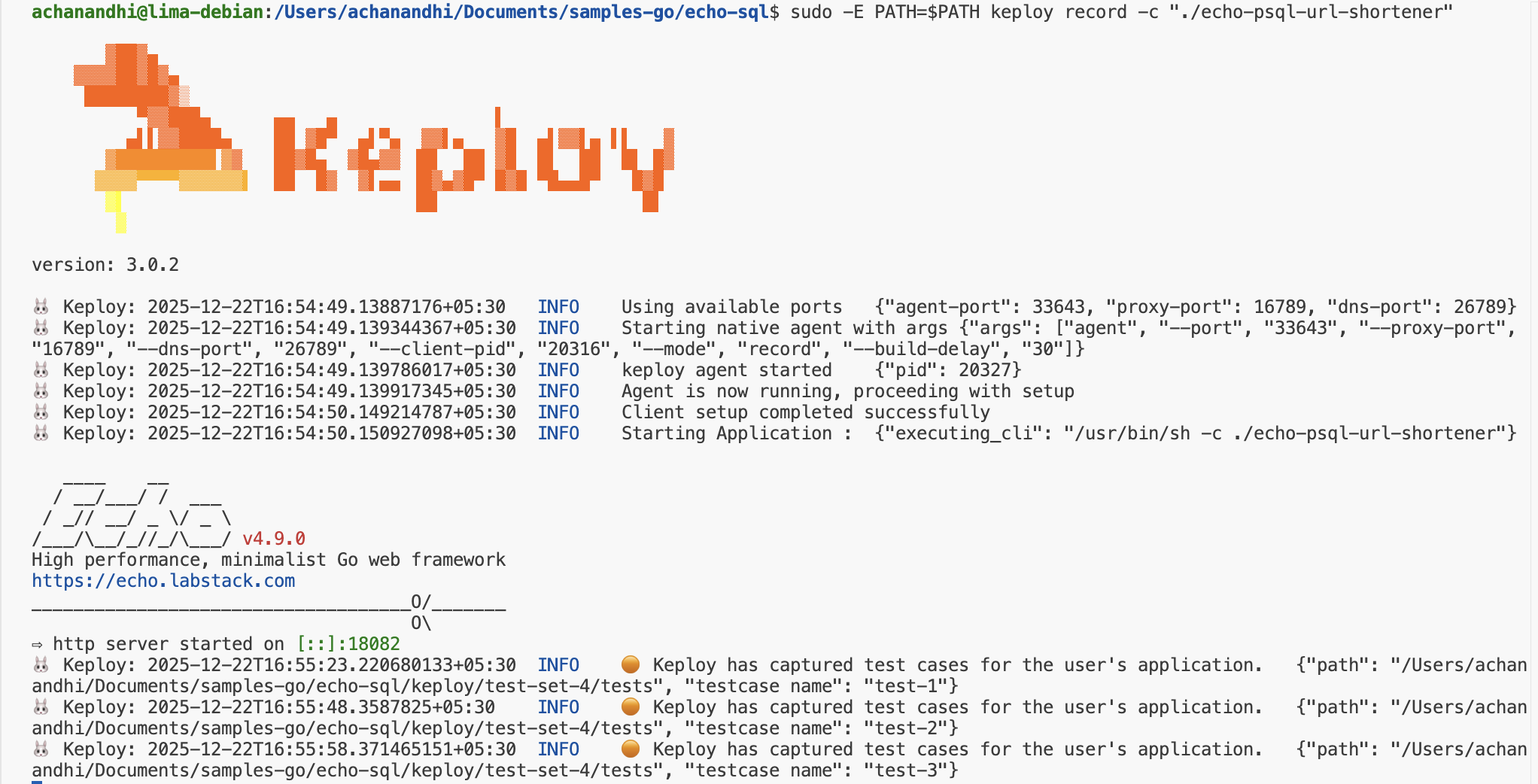
Capture the Testcases
sudo -E PATH=$PATH keploy record -c "./echo-psql-url-shortener"
Generate testcases
To genereate testcases we just need to make some API calls. You can use Postman, Hoppscotch, or simply curl
curl --request POST \
--url http://localhost:8082/url \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{
"url": "https://google.com"
}'
this will return the shortened url.
{
"ts": 1645540022,
"url": "http://localhost:8082/Lhr4BWAi"
}
Redirect to original url from shòrtened url
curl http://localhost:8082/Lhr4BWAi
or by querying through the browser http://localhost:8082/Lhr4BWAi
Now, let's see the magic! 🪄💫
Now both these API calls were captured as a testcase and should be visible on the Keploy CLI. You should be seeing an app named keploy folder with the test cases we just captured and data mocks created
Run the captured testcases
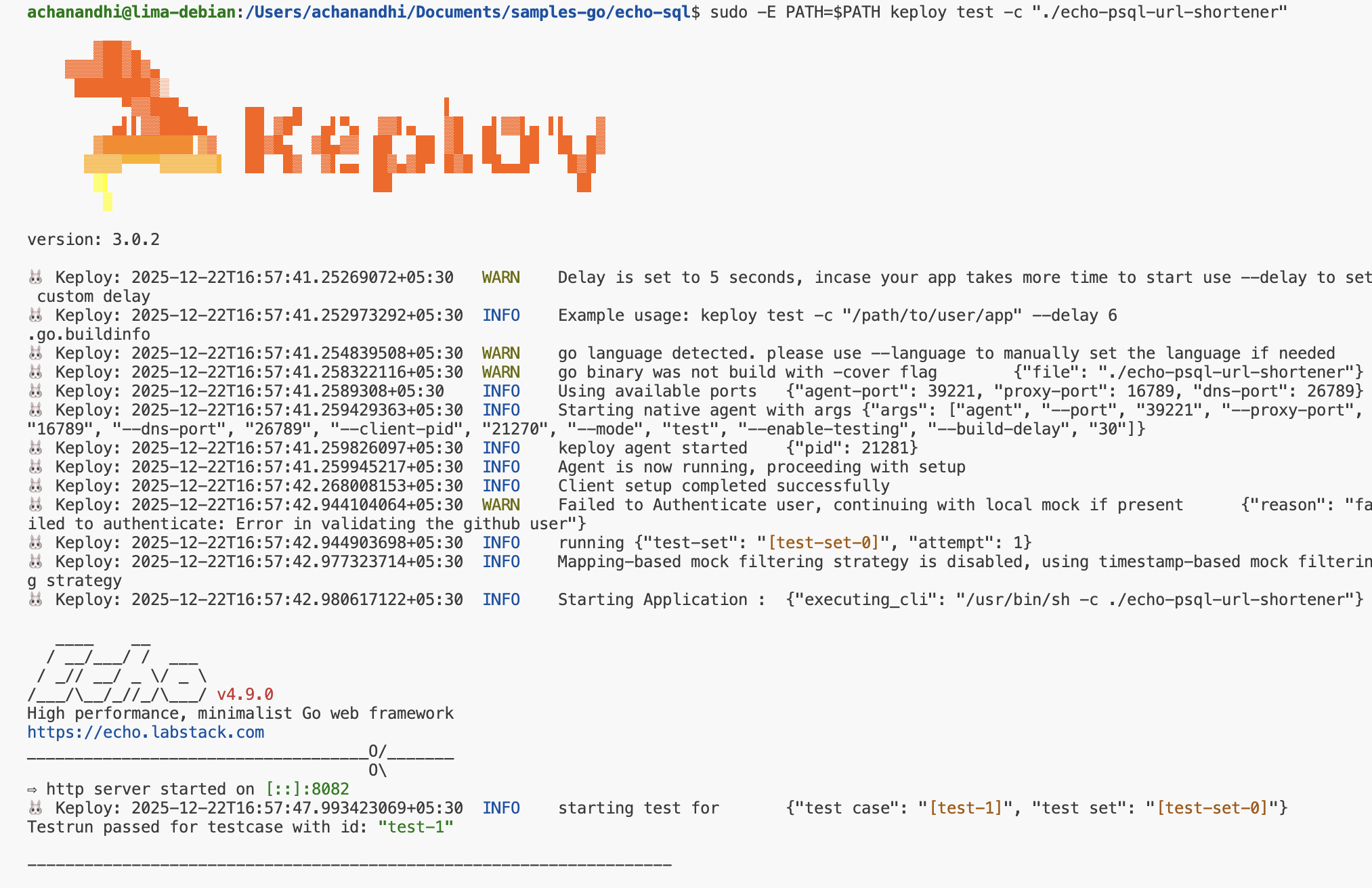
Now that we have our testcase captured, run the test file.
sudo -E PATH=$PATH keploy test -c "./echo-psql-url-shortener"
So no need to setup dependencies like postgres, web-go locally or write mocks for your testing.
The application thinks it's talking to postgres 😄
We will get output something like this:
Wrapping it up 🎉
Congrats on the journey so far! You've seen Keploy's power, flexed your coding muscles, and had a bit of fun too! Now, go out there and keep exploring, innovating, and creating! Remember, with the right tools and a sprinkle of fun, anything's possible.😊🚀
Hope this helps you out, if you still have any questions, reach out to us .