Keploy with OpenHospital
This is a openhospital app where you can record testcases and mocks by interacting with the UI, and then test them using Keploy.
This project has Three parts - the UI, Core and API, since Keploy is a backend testing platform, we need to start the Backend of the project using Keploy and run the frontend as it is.
Don’t have Keploy installed yet?
Before running this sample, make sure Keploy is installed on your system.
👉 Go to Installation GuideSetup the Core
git clone https://github.com/keploy/openhospital-core
cd openhospital-core/
git checkout integration-with-keploy
mvn clean install -DskipTests=true
docker compose up
Note: If you face any issues while setting up the database, please try running docker compose up again. The issue should not occur the second time.
Setup the Backend
Now it's time to setup the backend of our application. Let's Install the Openhospital API and get started.
git clone https://github.com/keploy/openhospital-api
cd openhospital-api/
git checkout integration-with-keploy
mvn clean install -DskipTests=true
Now it's time to start the Backend using Keploy cli:
Instructions For Starting Using Binary
Prerequisites For Binary:
- Node 20.11.0 LTS
- OpenJDK 17.0.9
- MVN version 3.6.3
Recording the testcases with Keploy
keploy record -c "java -cp "target/openhospital-api-0.1.0.jar:rsc/:static/" org.springframework.boot.loader.launch.JarLauncher"
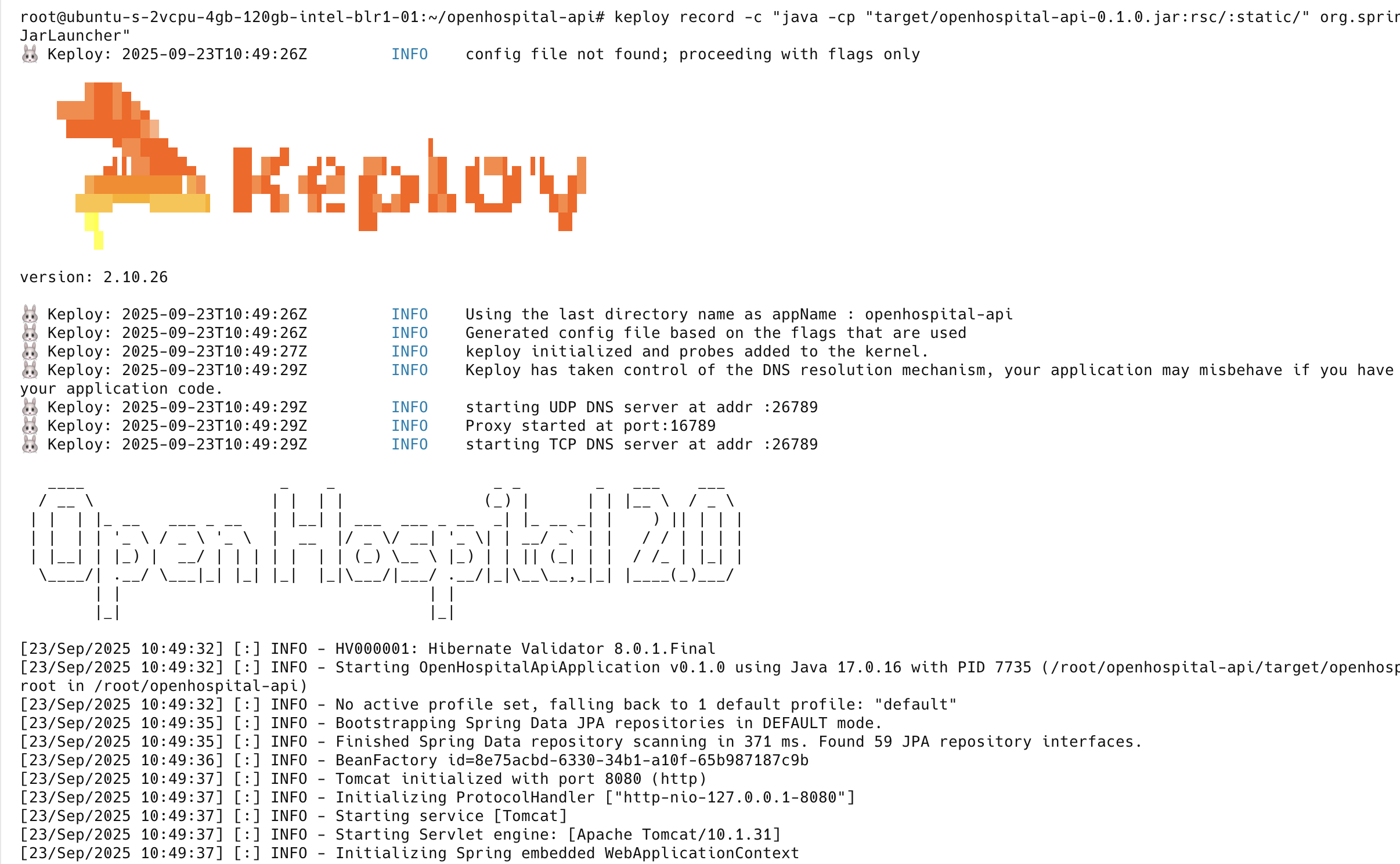
Start the frontend
git clone https://github.com/keploy/openhospital-ui
cd openhospital-ui/
git checkout integration-with-keploy
npm install
npm start
Note: Login with username admin and password admin
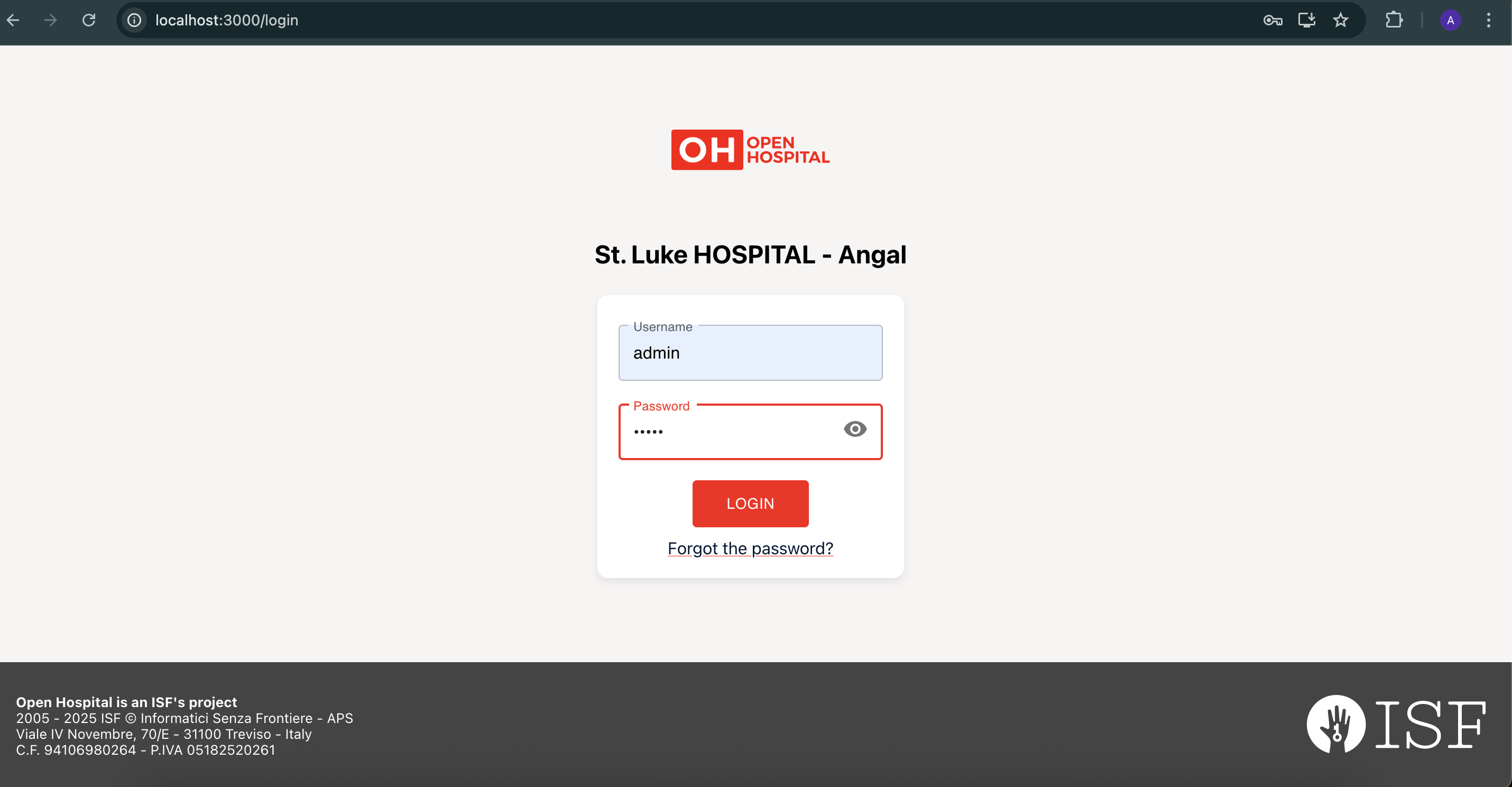
If you followed all the steps correctly, you should see a UI similar to the one shown above.
Now you can start interacting with the UI and Keploy will automatically create the testcases and mocks for it in a folder named 'keploy'
Running the testcases using Keploy
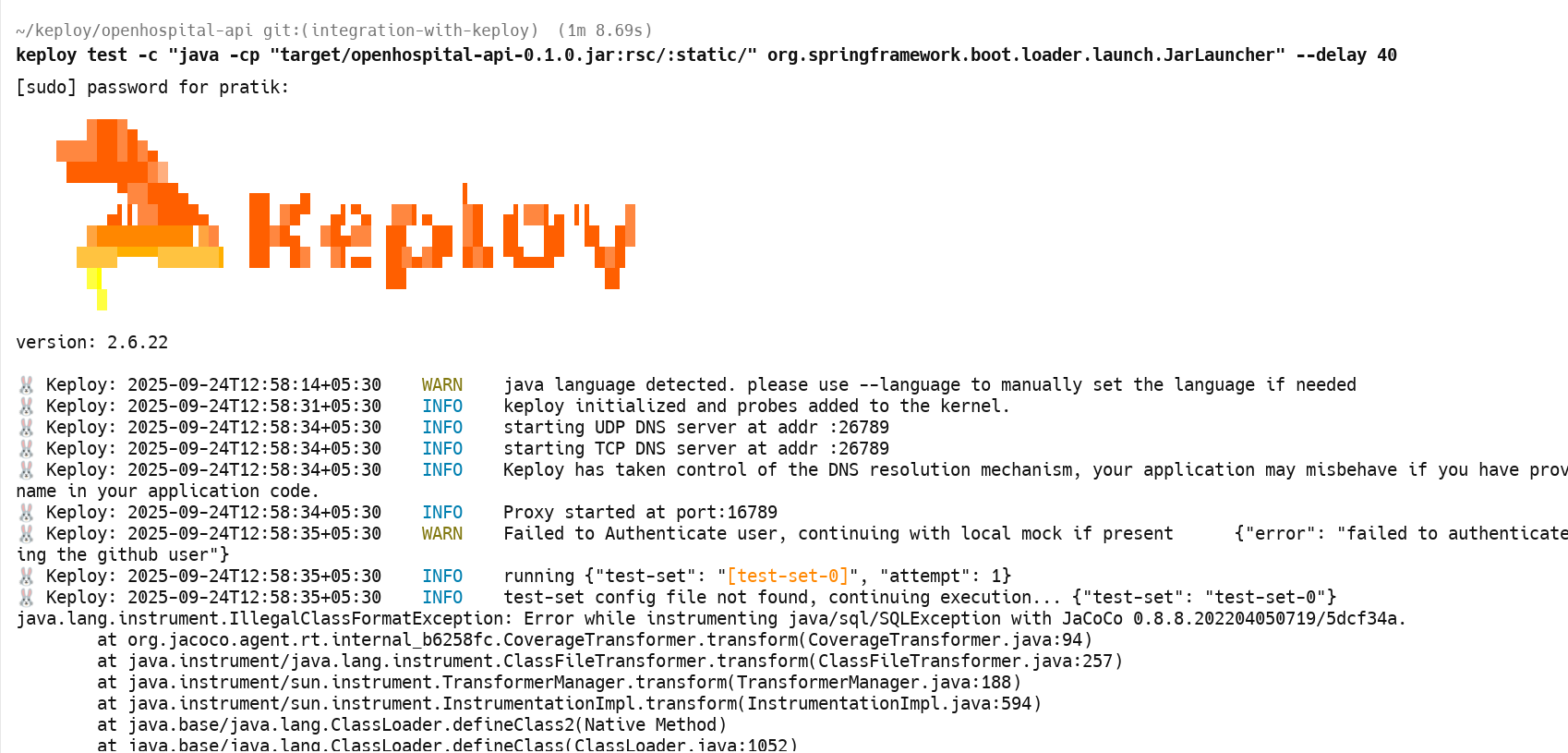
keploy test -c "java -cp "target/openhospital-api-0.1.0.jar:rsc/:static/" org.springframework.boot.loader.launch.JarLauncher" --delay 40
��🎉 Hooray! You've made it to the end of the binary section! 🎉
Your CLI should look something like this
This is a summary of the test cases recorded
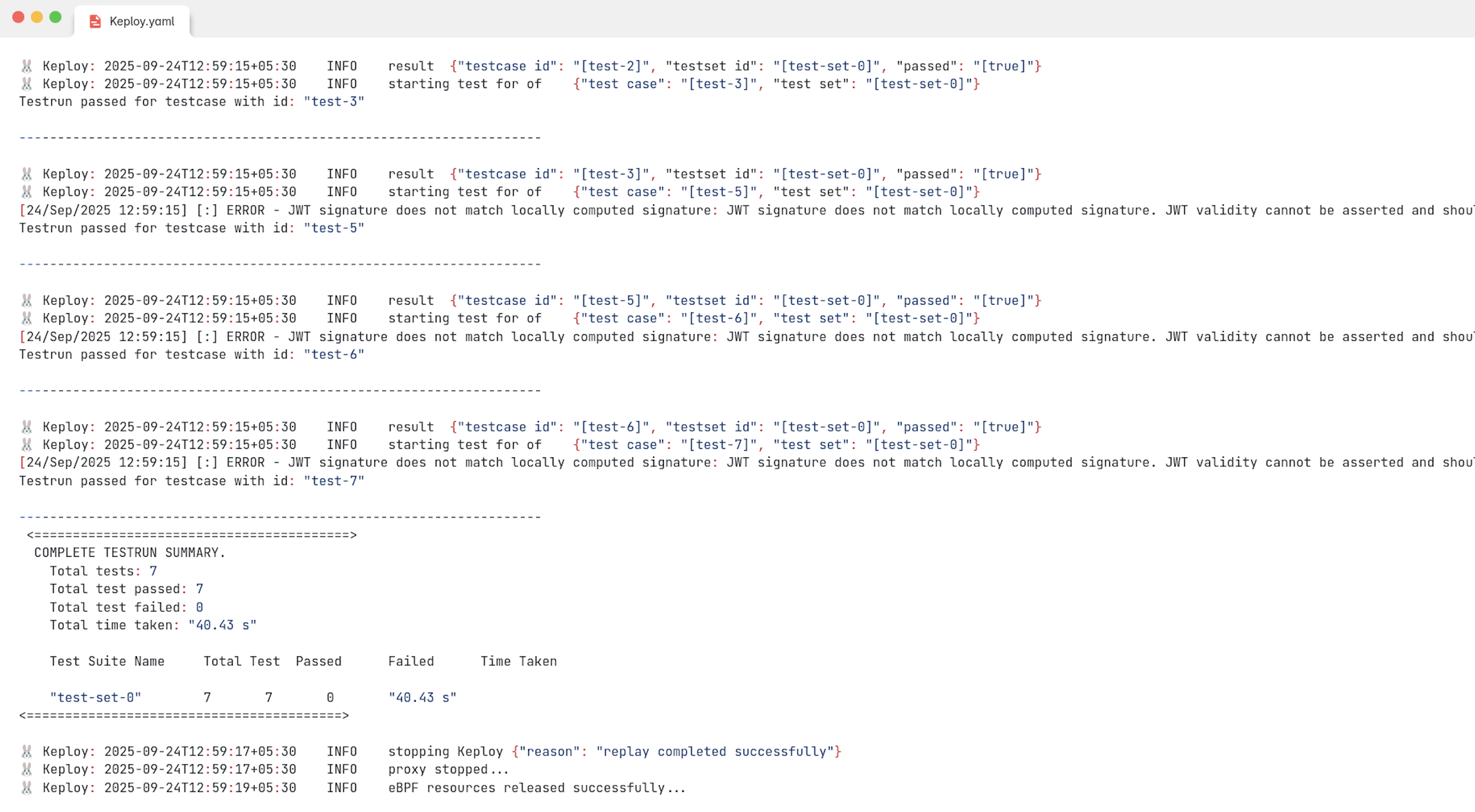
Here delay is the time it takes for your application to get started, after which Keploy will start running the testcases. If your application takes longer than 10s to get started, you can change the delay accordingly.
buildDelay is the time that it takes for the image to get built. This is useful when you are building the docker image from your docker compose file itself.
Hope this helps you out, if you still have any questions, reach out to us .